Mohtaram Ahmadbila and Ferrari10 Sahibaan (ahmadbila and ferrari10 ),
Today I will explain to you what the two terms (torque and horsepower) are. Both are related to each other. Remember one thing when it comes to engines. Torque is always measured and horsepower is always calculated. I'll explain this relationship later.
1. Torque: Torque is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum or pivot. Look at the figure below:
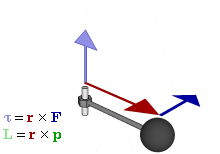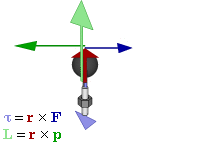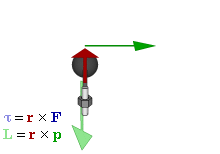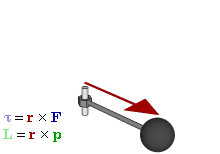
Torque is denoted by the Greek letter tau. Torque = r X F, where r is the lever arm and F is the force applied. Torque is the cross product of 'lever arm (r)' and force applied (F). If a one pound of force is applied at 2 feet of lever arm then the torque is 2 pounds feet (in the FPS, foot, pound, second system, also called the Imperial or British System). In the MKS (meter, kilogram, second or the International SI) system the units are Newton meters. The larger the force the greater the torque. The larger the lever arm, the greater the torque.
2. Power: Power is the rate of doing work or work done in a unit time. Horsepower is the unit of doing work in unit time in the FPS or Imperial System. In the MKS or SI system the units are Watts. We will stick to the FPS system for simplicity.
3. Work: Work = force X distance. If you expend one pound of force while moving an object one foot then work done is 1 pound foot.
Relation between Power and Work: The relationship between work and power is related to time. If your friend moves one pound of weight across one foot in two seconds and you move it in one second then you are twice as powerful. You have twice the power. Both of you have done the same amount of work but the guy doing it in lesser time will be more powerful. Therefore:
Power = force X distance/time. Whereas force X distance is work, so Power = work/time.
Horsepower: Horsepower = 33000 pound X feet/minutes. So if you move 33000 pounds across one foot in one minute then you have one horsepower of power.
Relationship between torque and horsepower. Here is another equation:
Horsepower = torque X rpm/5252. At 5252 revolutions per minute the engine's horsepower equals its torque. At 2 X 5252 = 10504 rpm horsepower is twice the torque, i.e horsepower = torque X 2, i.e. horsepower = 2 X torque at 10504 rpm (10504 is an rpm of academic interest only for it is very high).
Now please look at the following graph to understand the relationship between torque and horsepower:
Now I will explain to you the relationship between horsepower and torque. The horsepower is denoted by the red line and the torque by the blue one. Both are represented by the y axis (vertical line) and engine rpm is represented by the x axis (the horizontal line). Note that at engine rpm 5252 both torque and horsepower are the same. You measure both the horsepower and torque at the flywheel of the engine i.e. you take the transmission and differential out of the system and measure the quantity at the flywheel.
How do you measure torque? You measure it with an engine dynamometer. It is an equipment used to measure the torque and rpm at the the flywheel.
How to measure horsepower? Now you take both the readings (torque and rpm) and plug them into this equation:
Horsepower = torque X rpm/5252. Remember I told you that torque is measured (with a dynamometer) and horsepower is calculated (through this equation: horsepower = torque X rpm/5252).
If you look at the graph below, you will notice that torque is always higher than horsepower of the engine below 5252 rpm. Once you cross 5252 rpm horsepower is always higher than torque.
When do you need higher torque? We need higher torque to pull things like towing heavy weights. The best is a diesel engine which produces more torque at very low RPMs. So you don't have to rev up your engine to produce high torque as you would have to do if you had a gasoline engine.
When do you need high horsepower? You need high horsepower to accelerate your sports car. High RPMs give you high horsepower which is translated into more speed.
Diesel engines have a very high compression ratios (14:1 to 25:1) and low rpm. Gasoline engines have lower compression ratios (8:1 to 12:1) and high rpm. A higher compression ratio of a diesel engine means a higher torque because of the higher stroke (the length the piston travels in the cylinder) of the diesel which is translated into a higher diameter of the crankshaft giving us a higher lever arm producing more torque. Remember Torque = force X lever arm.
Watch this animation of a diesel engine to notice the higher stroke (high compression ratio) giving us high torque: HowStuffWorks "Diesel Engines vs. Gasoline Engines"
Watch this animation of a gasoline engine to note the lower stroke (low compression ratio) giving us low torque: HowStuffWorks "Internal Combustion"
The maximum horsepower or torque rating of an engine given in the brochure (of an engine) is measured at the flywheel. If you measure the two quantities at the wheels of a vehicle, they will be lower because of friction losses in the system (transmission, differential etc.)
1 Horsepower (FPS system) = 746 Watts (MKS system)
Please let me know if you need more explanation to make things clearer.
Any questions please?
Regards.
